Deposit Insurance
- For example: If a person has a deposit with a principal amount of Rs. 95,000/- and the interest on that amount is Rs. 4,000/-, then the total amount insured by DICGC is Rs. 99,000/-, however, if the principal amount is Rs. 1,00,000/- the further interest accrued will not be insured as the threshold on insurance cover is Rs. 1,00,000/- only.
- Consequently, the title of Deposit Insurance Act, 1961 was changed to 'The Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961 '. Effective from April 1, 1981, the Corporation extended its guarantee support to credit granted to small scale industries also, after the cancellation of the Government of India's credit guarantee scheme.
- Under Section 11 of the DICGC Act, 1961, all new commercial banks are required to be registered as soon as may be after they are granted licence by the Reserve Bank of India under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Banks covered by Deposit Insurance Scheme
Bonus code: THEBIGFREECHIPLIST. Casino name: Mandarin Palace Casino. 61 free spins with Trick or Treat. No multiple accounts or free bonuses in a row are allowed. If your last transaction was a free bonus please make a deposit before using this bonus. 40X Rollover needed. $100 You can cash out. Valid for all players. Exp: January 31, 2019. Thebigfreechiplist 2019. MegaSlot Affiliates. The affiliate program of Thebigfreechiplist Bonus Codes this gambling site Thebigfreechiplist Bonus Codes is run by MegaPartners Affiliates, a program that has been running since a years. With this program, you will Thebigfreechiplist Bonus Codes be able to claim commissions of up to 50%. The percentage you get from the affiliate program will Thebigfreechiplist Bonus Codes. Chipy.com is the World's Biggest and Most Reliable Source of Online Casino Bonus Codes, Reviews & Games! Join a Huge Community of Real Gamblers! Thebigfreechiplist 180 Free Spins Casino - Casino Bonuses THEBIGFREECHIPLIST Ruby Fortune. 30x Play through € 703000 Max cash out.
On liquidation etc. Of other de-registered banks i.e. Banks which have been de-registered on other grounds such as non payment of premium or their ceasing to be eligible co-operative banks under section 2(gg) of the DICGC Act, 1961, the Corporation will have no liability.
(I) All commercial banks including the branches of foreign banks functioning in India, Local Area Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
(II) Co-operative Banks - All eligible co-operative banks as defined in Section 2(gg) of the DICGC Act are covered by the Deposit Insurance Scheme. All State, Central and Primary co-operative banks functioning in the States/Union Territories which have amended their Co-operative Societies Act as required under the DICGC Act, 1961, empowering RBI to order the Registrar of Co-operative Societies of the respective States/Union Territories to wind up a co-operative bank or to supersede its committee of management and requiring the Registrar not to take any action for winding up, amalgamation or reconstruction of a co-operative bank without prior sanction in writing from the RBI, are treated as eligible banks. At present all Co-operative banks are covered by the Scheme. The Union Territories of Lakshadweep and Dadra and Nagar Haveli do not have Co-operative Banks.
Spin master coins free slots.
Registration of new banks as insured banksz
Under Section 11 of the DICGC Act, 1961, all new commercial banks are required to be registered as soon as may be after they are granted licence by the Reserve Bank of India under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Following the enactment of the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976 all Regional Rural Banks are required to be registered within 30 days from the date of their establishment in terms of Section 11A of the DICGC Act, 1961.
Co-operative Banks - A new co-operative bank is required to be registered as soon as may be after it is granted a licence by the RBI.
A primary co-operative credit society becoming a primary co-operative bank is to be registered within 3 months from the date of its application for licence.
A co-operative bank which has come into existence after the commencement of the Deposit Insurance Corporation (Amendment) Act, 1968, as a result of the division of any other co-operative society carrying on business as a co-operative bank, or the amalgamation of two or more co-operative societies carrying on banking business at the commencement of the Banking Laws (Application to Co-operative Societies) Act, 1965 or at any time thereafter is to be registered within three months of its making an application for licence.
However, a co-operative bank will not be registered, if it has been informed by the RBI in writing that a licence cannot be granted to it.
In terms of Section 14 of the DICGC Act, after the Corporation registers a bank as an insured bank, it is required to send, within 30 days of the bank's registration, an intimation in writing to the bank that it has been registered as an insured bank.
The letter of intimation, apart from the advice of registration and registration number, gives the details about the requirements to be observed by the bank, the rate of premium payable to the Corporation, the manner in which the premium is to be paid by the bank and the returns to be furnished to the Corporation etc. The insured bank has to submit its first return and remit the amount of premium within one month from the receipt of the letter, which is dispatched by Registered post or the date of commencement of business whichever is later. A copy of this letter is endorsed to the Reserve Bank of India and also National Bank For Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) in the case of Regional Rural Banks/State co-operative banks and District Central co-operative banks.

Insurance coverage
IInitially, under the provisions of Section 16(1) of the DICGC Act, the insurance cover was limited to 1,500/- only per depositor(s) for deposits held by him (them) in the 'same right and in the same capacity' in all the branches of the bank taken together. However, the Act also empowers the Corporation to raise this limit with the prior approval of the Central Government. Accordingly, the insurance limit was enhanced from time to time as follows:
>> 5,000/- with effect from 1st January 1968
>> 10,000/- with effect from 1st April 1970
>> 20,000/- with effect from 1st January 1976
>> 30,000/- with effect from 1st July 1980
>> 1,00,000/- with effect from 1st May 1993 onwards.
Types of Deposits Covered
DICGC insures all bank deposits, such as saving, fixed, current, recurring, etc. except the following types of deposits.
(i) Deposits of foreign Governments;
(ii) Deposits of Central/State Governments;
(iii) Inter-bank deposits;
(iv) Deposits of the State Land Development Banks with the State co-operative banks;
(v) Any amount due on account of and deposit received outside India;
(vi) Any amount which has been specifically exempted by the corporation with the previous approval of the RBI.
| निक्षेप बीमा और प्रत्यय गारंटी निगम | |
| Credit and Insurance Institution overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 1978; 43 years ago |
| Headquarters | Mumbai, India |
| Credit and Insurance Institution executive | |
| Key document |
|
| Website | www.dicgc.org.in |
Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Reserve Bank of India. It was established on 15 July 1978 under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961 for the purpose of providing insurance of deposits and guaranteeing of credit facilities.
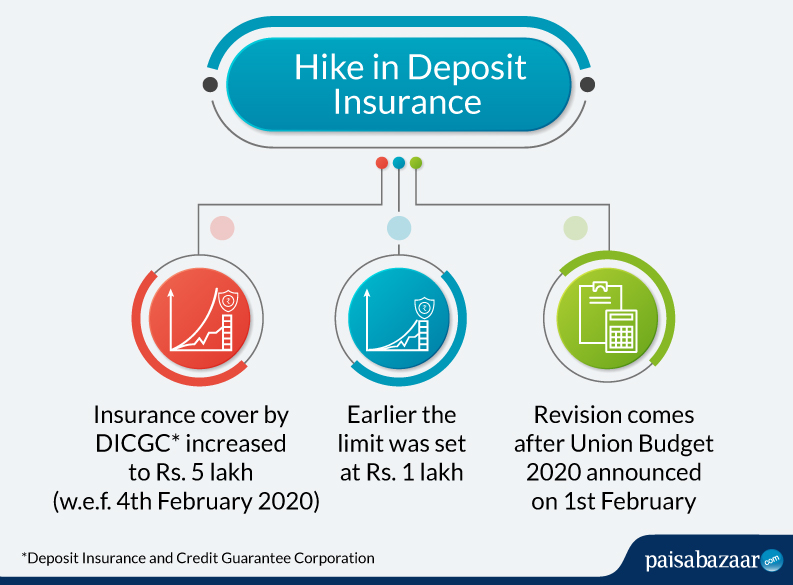
DICGC insures all bank deposits, such as saving, fixed, current, recurring deposit for up to the limit of Rs. 500,000 of each deposits in a bank.[1]

Framework[edit]
The functions of the subsidiary are governed by the provisions of 'The Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961' (DICGC Act) and 'The Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation General Regulations, 1961' framed by the Reserve Bank of India in exercise of the powers conferred by sub-section (3) of Section 50 of the Act.[2]
Play Video Slots Casino Online - Get 11 Free Spins! We would like to welcome you to our casino room and also tell you a bit about us. Videoslots always do its utmost to offer the best of online casino.You will. Video slots desktop site software. Welcome to Videoslots.com, the biggest online casino in the world. We have over 4,000 games in our portfolio, with titles covering all the different types of online slots available. We also offer scratch card. At Videoslots, we believe we’ve got the biggest selection of video slots you can find anywhere! Video slots work in the same way as online slots but are even more popular with players who prefer action.
A maximum of ₹5,00,000 (after the budget of 2020-21) is insured for each user for both principal and interest amount.If the customer has accounts in different branches of the same bank, all of those accounts are insured to a maximum of ₹5,00,000 each.


However, if there are more accounts in same bank, all of those are treated as a single account.The insurance premium is paid by the insured banks itself. This means that the benefit of deposit insurance protection is made available to the depositors or customers of banks free of cost.
The Corporation has the power to cancel the registration of an insured bank if it fails to pay the premium for three consecutive half-year periods.The Corporation may restore the registration of the bank if the bank makes a request and pays all the amounts due by way of premium from the date of default together with interest.
Dicgc Act
Reforms[edit]
Dicgc Rules
The Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission (FSLRC) was set up by the Government of India, Ministry of Finance, on 24 March 2011, to review and rewrite the legal-institutional architecture of the Indian financial sector. In its report the FSLRC recommended a regulatory structure consisting of seven agencies including a deposit insurance-cum regulatory agency (which was named as Resolution Corporation). The present DICGC will be subsumed into the Resolution Corporation (RC) which will work across the financial system.
Dicgc Act Upsc
Drawing on the best international practice, the FSLRC proposal involved a unified resolution corporation that will deal with an array of financial firms such as banks and insurance companies; it will not just be a bank deposit insurance corporation. It will concern itself with all financial firms which make highly intense promises to consumers, such as banks, insurance companies, defined benefit pension funds, and payment systems.
It will also take responsibility for the graceful resolution of systemically important financial firms, even if they have no direct links to consumers.[citation needed]
The Government of India introduced the Financial Resolution and Deposit Insurance bill, 2017 (FRDI bill) in Lok Sabha in the Monsoon session of 2017 to bring forth these reforms.[3] There have been many concerns with regards to the new bill such as:
- Presently the banks have to pay a sum to the DICGC as insurance premium which insures all kinds of bank deposits up to a limit of ₹5,00,000. In case a stressed bank had to be liquidated, the depositors would be paid through DICGC. Though the bill proposes the banks to pay a sum to the Resolution Corporation, it neither specifies the insured amount nor the amount a depositor would be paid. It is thus unclear how much a depositor would be paid in case of liquidation.
- The bail in clause which largely worked against the interests of the depositors (as in Cyprus).[4][clarification needed]
References[edit]
- ^'Srikrishna panel insists on single unified regulator in financial sector'. Business Standard. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 23 November 2013.
- ^'About Us - Profile'. .Dicgc. Archived from the original on 24 March 2013. Retrieved 23 November 2013.
- ^'PRS - Bill Track - The Financial Resolution and Deposit Insurance Bill, 2017'. www.prsindia.org. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^'The FRDI Bill and concerns of the depositor'. The Hindu. 29 November 2017.